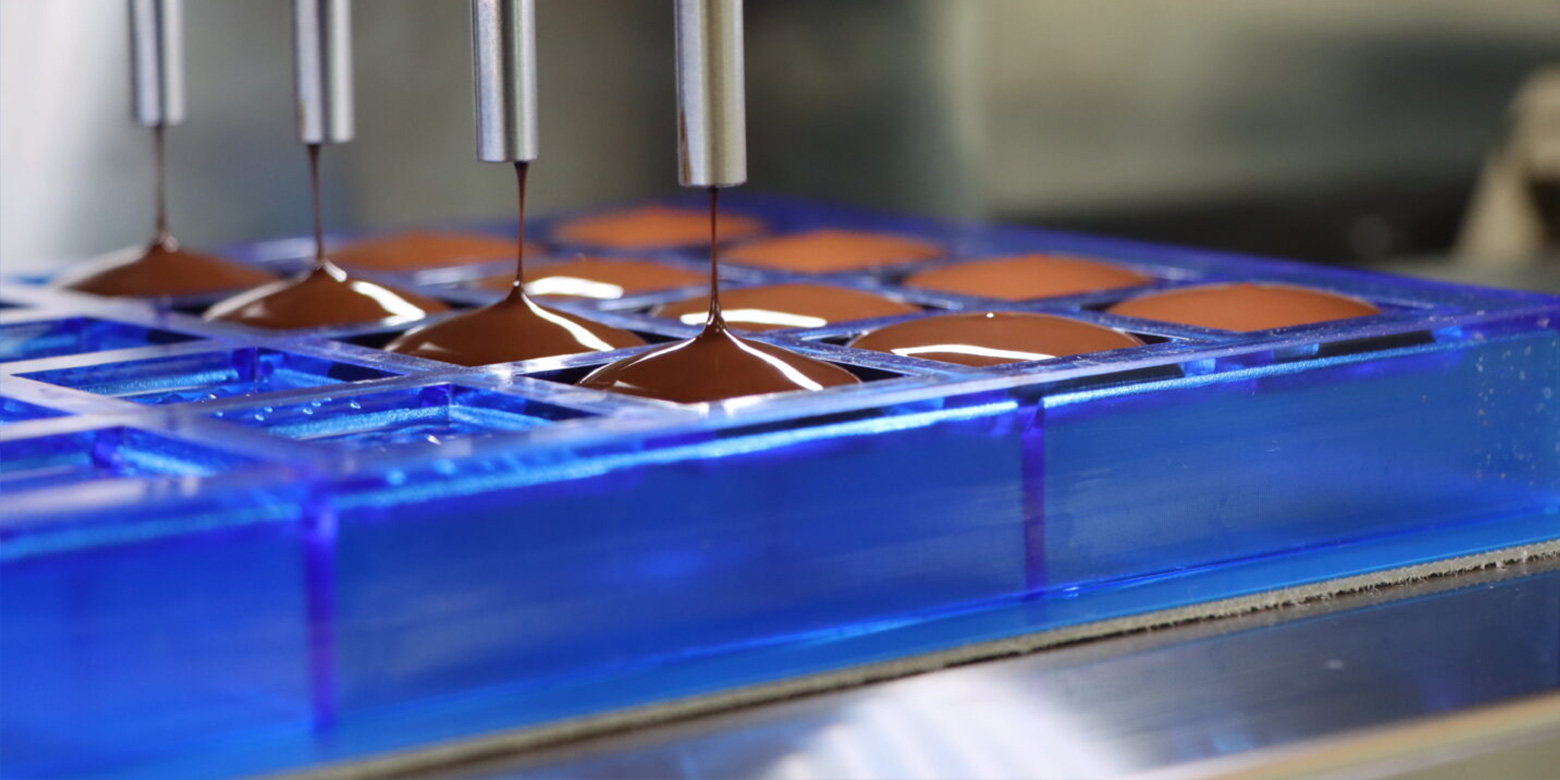
3D printing of special components with detectable plastics, for the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries
In the modern era of industrial manufacturing, 3D printing technology has revolutionized numerous industries. Among these, the food, cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries have taken advantage of the incredible possibilities offered for the production of special components with detectable plastics.
These plastics are designed to be easily identified and removed during quality controls, thus reducing the risk of product contamination and ensuring consumer safety.
In the context of the food, cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries, product safety is paramount. The use of components 3D printed with detectable plastic ensures that you can easily locate any fragments or parts that may detach from devices or packaging. The filaments contain contrast agents, such as metal or ceramic additives, which make the printed parts detectable to standard detection systems, such as metal detectors.
Detectable plastics used in 3D printing must meet strict food and pharmaceutical safety standards. They must be non-toxic, resistant to wear and corrosion, and easily workable. Through Additive Manufacturing there is the possibility to create prototypes and small series quickly and economically. This allows companies to always have spare parts in stock, which allow to reduce downtime in case of interruption of production lines. This ideology leads today to the concept of "digital warehouse", that is a set of files ready for in-house printing that guarantees a reduction in physical space in the warehouse.
So, what are the magneto detectable materials - used in Additive Manufacturing - that can be printed with a filament 3D printer? There are currently two types of polymers available:
- PETG Magneto Detectable
- PA Blue Metal Detectable
PETG MDT
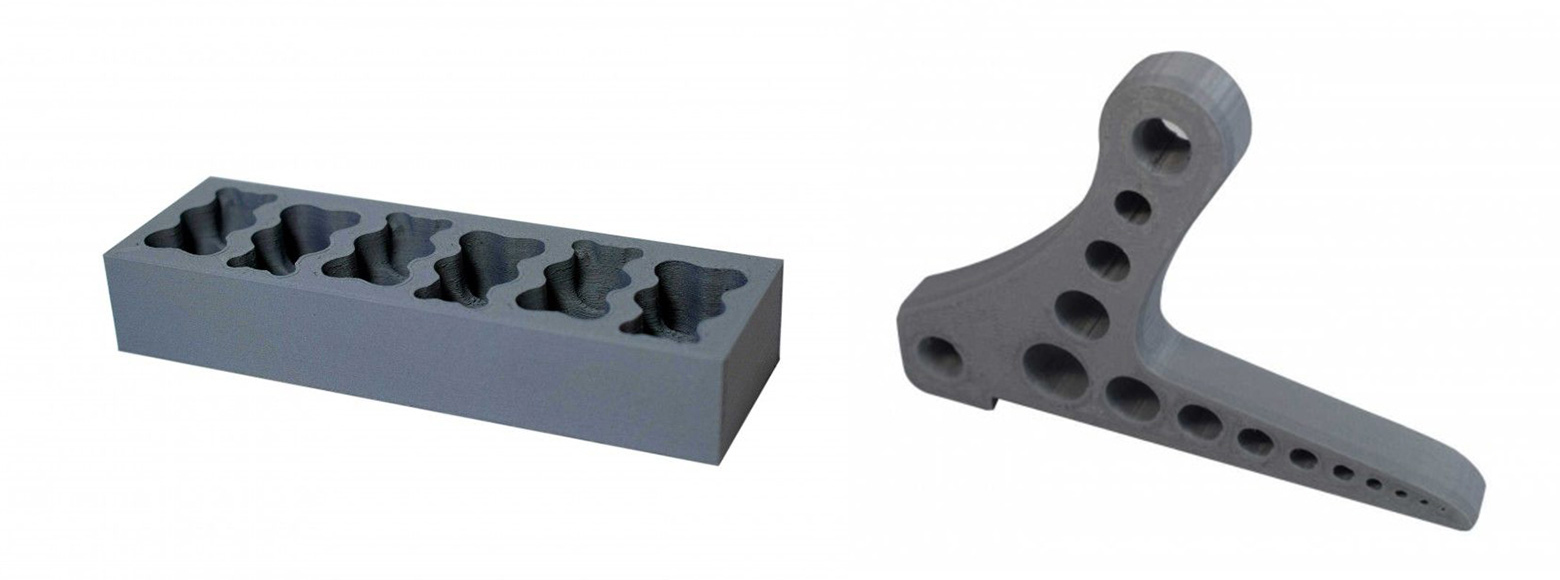

PETG MDT is manufactured by adding a detectable additive that allows a standard metal detector, placed at a specific point in the production line, to detect fragments in the event that a plastic component breaks during production. Furthermore, this filament has a high dimensional stability, typical of PETG-based materials, and it is very easy to print at temperatures between 220 °C and 240 °C, preferably with steel nozzles or ruby tip (ideal for abrasive materials) and print bed around 85 °C. Among other characteristics, the material, which is not hygroscopic, resists moisture, fungus and mold.
Viable applications are sensors, intelligent packaging, molds, and conveyor components.
PA Blue MDT
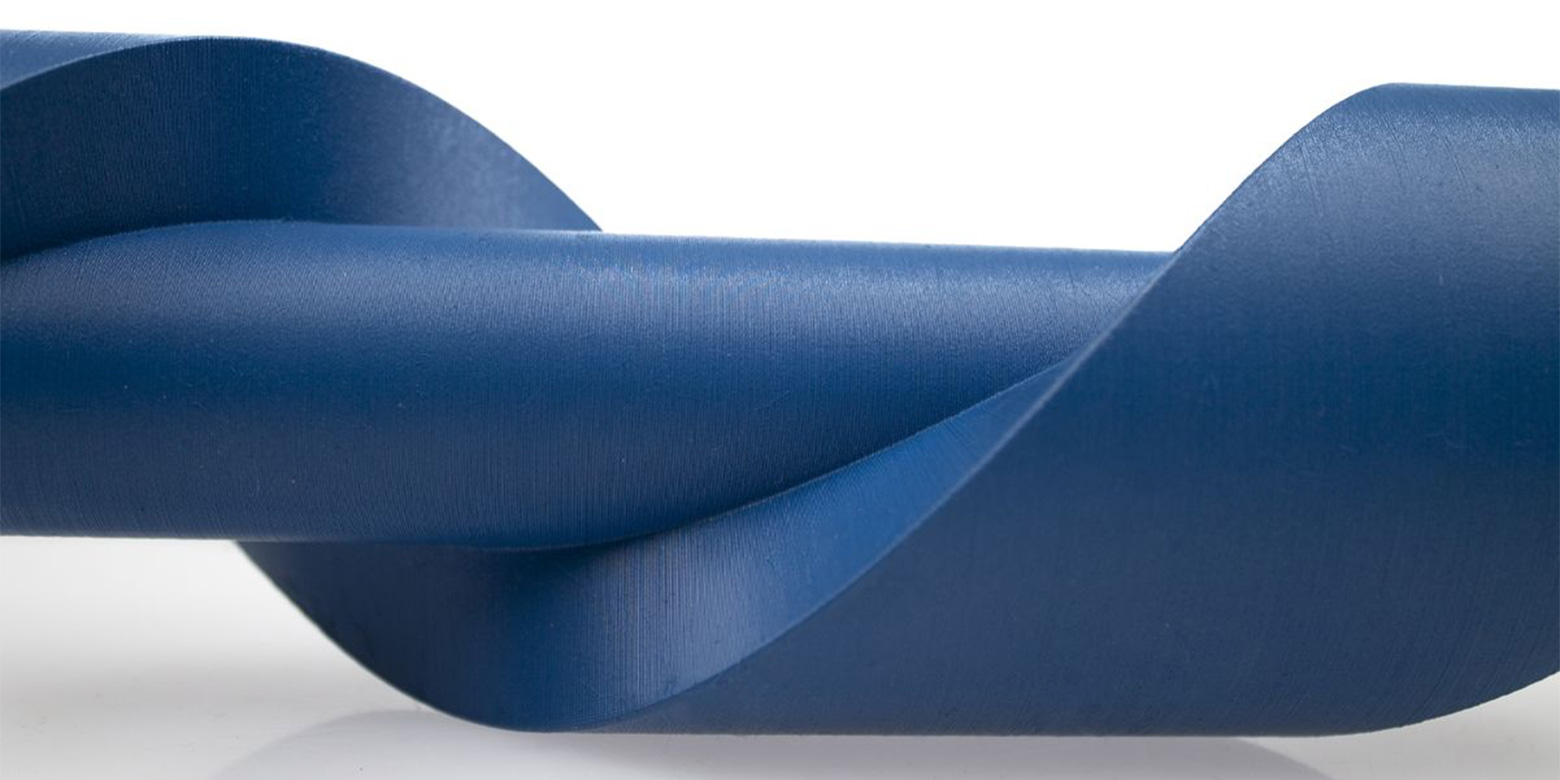

Recently, a blue polyamide that is also detectable by metal detectors has been developed.
Blue is chosen as the common color for plastics because it offers a high visual contrast compared to most food products. This makes it easier for workers and visualization systems to detect any plastic fragments.
The Nylon based polymer has been approved for food contact according to Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 in terms of specific measures for groups of materials – in this case, plastics – in the form of Regulation (EU) No 10/2011.
In addition, it complies with Regulation (EC) No 2023/2006 (Articles 5, 6 and 7). The components and monomers of the product are listed in Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as amended.
Overall, the use of blue color is a proactive approach to prevent, detect and mitigate potential product contamination, maintaining high food safety standards, protecting consumer health and ensuring the integrity of production processes. There are plastic compounds and metal-detectable elastomers able to satisfy both the technological needs of the sector and comply with the necessary hygiene regulations. However, optical detection remains the most economical control method and continues to prove successful in a still quite wide range of applications that can be developed through metal-detectable materials.


Not only food&beverage
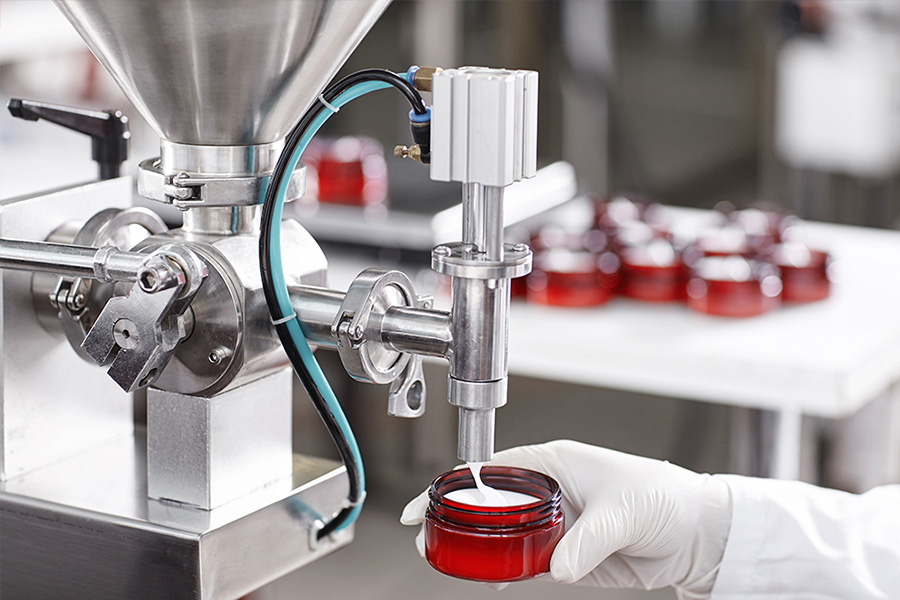
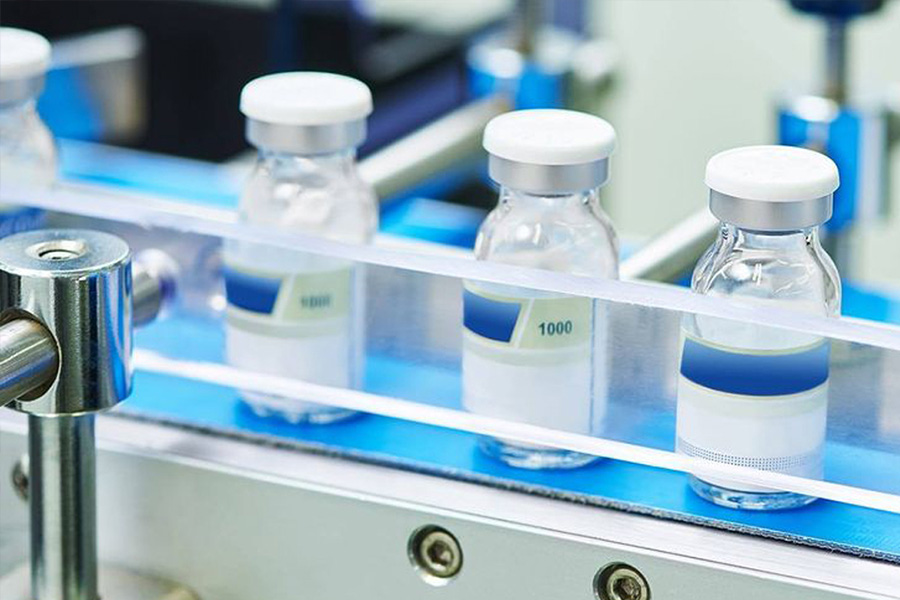
The use of MDT polymers does not only concern the food sector, but also pharmaceutical and cosmetic for the realization of tailor-made cosmetics, personalized medical devices and pharmaceutical dosages adapted to the needs of the patient.
3D printed applications focus more on components or spare parts for inspection and quality control systems for commercial products. The quality of the final product is also the number one priority in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry, as possible contamination could reduce the quality itself or even damage the health of the consumer.